Introduction
Using tools like hydra, medusa or ncrack, an attacker can try to find out the password of a particular service.
Sometimes you may want to better understand the technology behind it.
For example, you just want to check how a tool works if you’ve set a specific credential for a service. Does it show the right information? How does it show it?
Or you want to go deeper and understand better what runs behind the scenes using verbose or debug mode at those tools on a service configured by you. But it should not be too complicated. Just one you can fire up fast and throw it away afterwards.
For this purpose, it would be nice to be able to quickly start up a service for testing, but only run it locally on the computer.
A nice way to do this is using docker.
The following text summarizes dockerized protocols/services based upon password authentication. It’s a gathering of different Dockerfiles for use in testing online cracking tools with corresponding examples. Something like a “dockerized service collection to test online cracker”. This text comprises 8 protocols:
- http-basic-auth
- http-digest-auth
- ssh
- imap
- smtp
- ftp
- rdp
- vnc
Every Dockerfile you can start an run attacks against it. Sometimes an attacking tool didn’t work for me in which case I omitted it in the corresponding section.
For credentials to test you can use https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists or use the known credentials like I did in the latter examples.
You can add these parameters if you want to have more information in the output (maximum verbose and debug level):
medusa:
-v 6 -w 10
ncrack:
-vvv -d10
hydra:
-v -V -d
HTTP
For HTTP Server running Basic or Digest Authentication can be started and attacked in the following way:
Basic Authentication
A possible Dockerfile looks like this:
cat Dockerfile.http_basic_auth
FROM nginx:1.21.3
LABEL maintainer="secf00tprint"
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y apache2-utils
RUN touch /usr/share/nginx/html/.htpasswd
RUN htpasswd -db /usr/share/nginx/html/.htpasswd test password
RUN sed -i '/^ location \/ {/a \ auth_basic "Administrator\x27s Area";\n\ auth_basic_user_file /usr/share/nginx/html/.htpasswd;' /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
You can run it the following way:
sudo docker build -f Dockerfile.http_basic_auth -t http-server-basic-auth .
sudo docker run -ti -p 127.0.0.1:8888:80 http-server-basic-auth
and then attack it like this:
medusa -h 127.0.0.1 -n 8888 -u test -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt -M http -f
ncrack --user test -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt http://127.0.0.1:8888 -g path=/ -f
hydra -l 'test' -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt 127.0.0.1 -s 8888 http-get /
HTTP Digest Authentication
Here I deployed an nginx example which is based upon ngx_http_auth_digest module and another one using Flask.
nginx
For the nginx demo you need two files:
The Dockerfile
cat Dockerfile.http_digest_nginx
FROM ubuntu:20.10
LABEL maintainer="secf00tprint"
RUN apt-get update && \
# For digest module
DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y curl unzip \
# For nginx
build-essential libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zlib1g zlib1g-dev libssl-dev libgd-dev libxml2 libxml2-dev uuid-dev make apache2-utils expect
RUN curl -O https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.21.3.tar.gz
RUN curl -OL https://github.com/atomx/nginx-http-auth-digest/archive/refs/tags/v1.0.0.zip
RUN tar -xvzf nginx-1.21.3.tar.gz
RUN unzip v1.0.0.zip
RUN cd nginx-1.21.3 && \
./configure --prefix=/usr/share/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --pid-path=/run/nginx.pid --modules-path=/etc/nginx/modules --add-module=../nginx-http-auth-digest-1.0.0/ && \
make && make install
COPY generate.exp /usr/share/nginx/html/
RUN chmod u+x /usr/share/nginx/html/generate.exp && \
cd /usr/share/nginx/html/ && \
expect -d generate.exp
RUN sed -i '/^ location \/ {/a \ auth_digest "this is not for you";' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
RUN sed -i '/^ location \/ {/i \ auth_digest_user_file /usr/share/nginx/html/passwd.digest;' /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
CMD nginx && tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
and the expect script to generate the digest password file:
cat generate.exp
#!/usr/bin/expect
set timeout 70
spawn "/usr/bin/htdigest" "-c" "passwd.digest" "this is not for you" "test"
expect "New password: " {send "password\r"}
expect "Re-type new password: " {send "password\r"}
wait
Then run:
sudo docker build -f Dockerfile.http_digest_nginx -t http_digest .
sudo docker run -ti -p 127.0.0.1:8888:80 http_digest
Afterwards you can attack the server as follows:
medusa -h 127.0.0.1 -n 8888 -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt -u test -M http -m AUTH:DIGEST
ncrack -u test -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt http://127.0.0.1:8888 -f
hydra -l 'test' -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt 127.0.0.1 -s 8888 http-get /
Flask
To anticipate: hydra cannot brute force Flask using their default documentation.
You can verify this using:
cat Dockerfile.http_digest_flask
FROM ubuntu:20.10
LABEL maintainer="secf00tprint@gmail.com"
RUN apt-get update -y && \
apt-get install -y python3-pip python3-dev
# We copy just the requirements.txt first to leverage Docker cache
COPY ./requirements.txt /app/requirements.txt
WORKDIR /app
RUN pip3 install -r requirements.txt
COPY ./app.py /app/
CMD ["flask", "run", "--host=0.0.0.0"]
cat requirements.txt
Flask==2.0.2
Flask-HTTPAuth==4.5.0
cat app.py
from flask import Flask
from flask_httpauth import HTTPDigestAuth
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = 'super secret key'
auth = HTTPDigestAuth()
users = {
"test" : "password",
"john" : "hello",
"susan" : "bye"
}
@auth.get_password
def get_pw(username):
if username in users:
return users.get(username)
return None
@app.route("/")
@auth.login_required
def hello_world():
return "Flask Digest Demo
"
sudo docker build -f Dockerfile.http_digest_flask -t digest_flask .
sudo docker run -ti -p 127.0.0.1:5000:5000 digest_flask
hydra -l 'test' -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt) 127.0.0.1 -s 5000 http-get / -f -V -W 10
SSH
To get a running ssh test service with password authentication you can use:
cat Dockerfile.ssh
FROM ubuntu:21.10
LABEL maintainer="secf00tprint"
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y vim openssh-server rsyslog
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
RUN sed -i 's/#PasswordAuthentication.*$/PasswordAuthentication yes/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
RUN useradd -ms /bin/bash test
RUN echo test:password | chpasswd
CMD service rsyslog start && service ssh start && tail -F /var/log/auth.log
sudo docker build -f Dockerfile.ssh -t sshs .
sudo docker run -ti -p 127.0.0.1:22:22 sshs
And then try to find the credentials using:
medusa -h 127.0.0.1 -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt -u test -M ssh
ncrack -u test -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt ssh://127.0.0.1 -f
hydra -l 'test' -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt 127.0.0.1 ssh
SMTP and IMAP
For SMTP and IMAP I created a fork and branch from https://github.com/antespi/docker-imap-devel.
You can inspect it here. It is based upon postfix and dovecot and needed a little more complicated setup.
After you clone it
git clone git@github.com:secf00tprint/docker-imap-devel.gitswitch to the right branch
git checkout password_protected_mail_serveryou can run it using:
sudo docker build -t mail-server .
sudo docker run -ti -p 127.0.0.1:25:25 -p 127.0.0.1:143:143 -p 127.0.0.1:993:993 mail-server
and start an attack with the following commands, they all only test the already known credentials.
If you want to change this you can add them to your wordlists. After that change the command line parameters corresponding to each online cracker which uses a wordlist not a single string.
STMP
hydra -l 'debug@localdomain.test' -p 'debug' -V -s 25 127.0.0.1 smtp
IMAP
ncrack imap://172.17.0.2:993 -m imap --user 'debug@localdomain.test' --pass 'debug' -g ssl
hydra -l 'debug@localdomain.test' -p 'debug' 127.0.0.1 imap -S
The last 2 protocols completely rely on external dockerhub implementations:
FTP
Based upon https://github.com/fauria/docker-vsftpd you can launch it with:
sudo docker run -d -p 127.0.0.1:20:20 -p 127.0.0.1:21:21 -p 127.0.0.1:21100-21110:21100-21110 \/
-e FTP_USER=user -e FTP_PASS=pass fauria/vsftpd
herear, for the test:
medusa -h 127.0.0.1 -M ftp -u 'user' -p 'pass'
ncrack --user user --pass pass 127.0.0.1:21
hydra -l user -p pass 127.0.0.1 ftp
RDP
For RDP you can use the docker image from Daniel Guerra:
sudo docker run -d --hostname terminalserver --shm-size 1g -p 127.0.0.1:3389:3389 -p 127.0.0.1:2222:22 danielguerra/ubuntu-xrdp:20.04
once running you can verify it with:
hydra -l ubuntu -p ubuntu 127.0.0.1 rdp
VNC
There is a nice github repo implementing different ubuntu flavors for VNC: docker-ubuntu-vnc-desktop.
You can run the server using:
sudo docker run -p 127.0.0.1:5900:5900 -e VNC_PASSWORD=password dorowu/ubuntu-desktop-lxde-vnc:focal
after that, scan the server with:
medusa -h 127.0.0.1 -n 5900 -u "" -p password -M vnc
ncrack --pass password vnc://127.0.0.1:5900 -f
hydra -p password -t 1 -w 5 -f -s 5900 127.0.0.1 vnc
To test that there is no blocking feature which sometimes is set in newer VNC servers run:
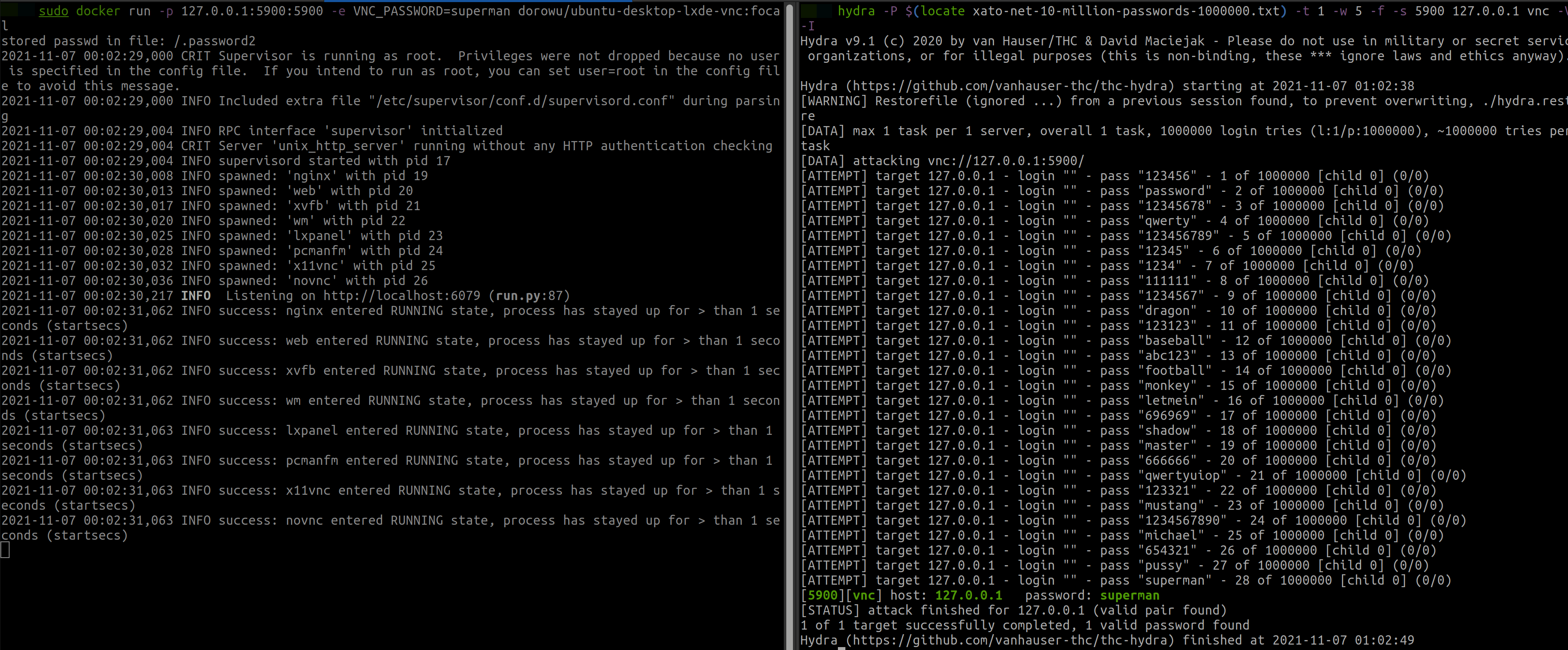
sudo docker run -p 127.0.0.1:5900:5900 -e VNC_PASSWORD=superman dorowu/ubuntu-desktop-lxde-vnc:focal
“superman” is position 30 in the xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt list.
hydra -P path_to/SecLists/Passwords/xato-net-10-million-passwords-1000000.txt) -t 1 -w 5 -f -s 5900 127.0.0.1 vnc -V -I
Summary
Hope you like it. If you have anything you don’t like or like or feedback for enhancement please write it to secf00tprint+blog@gmail.com :) .